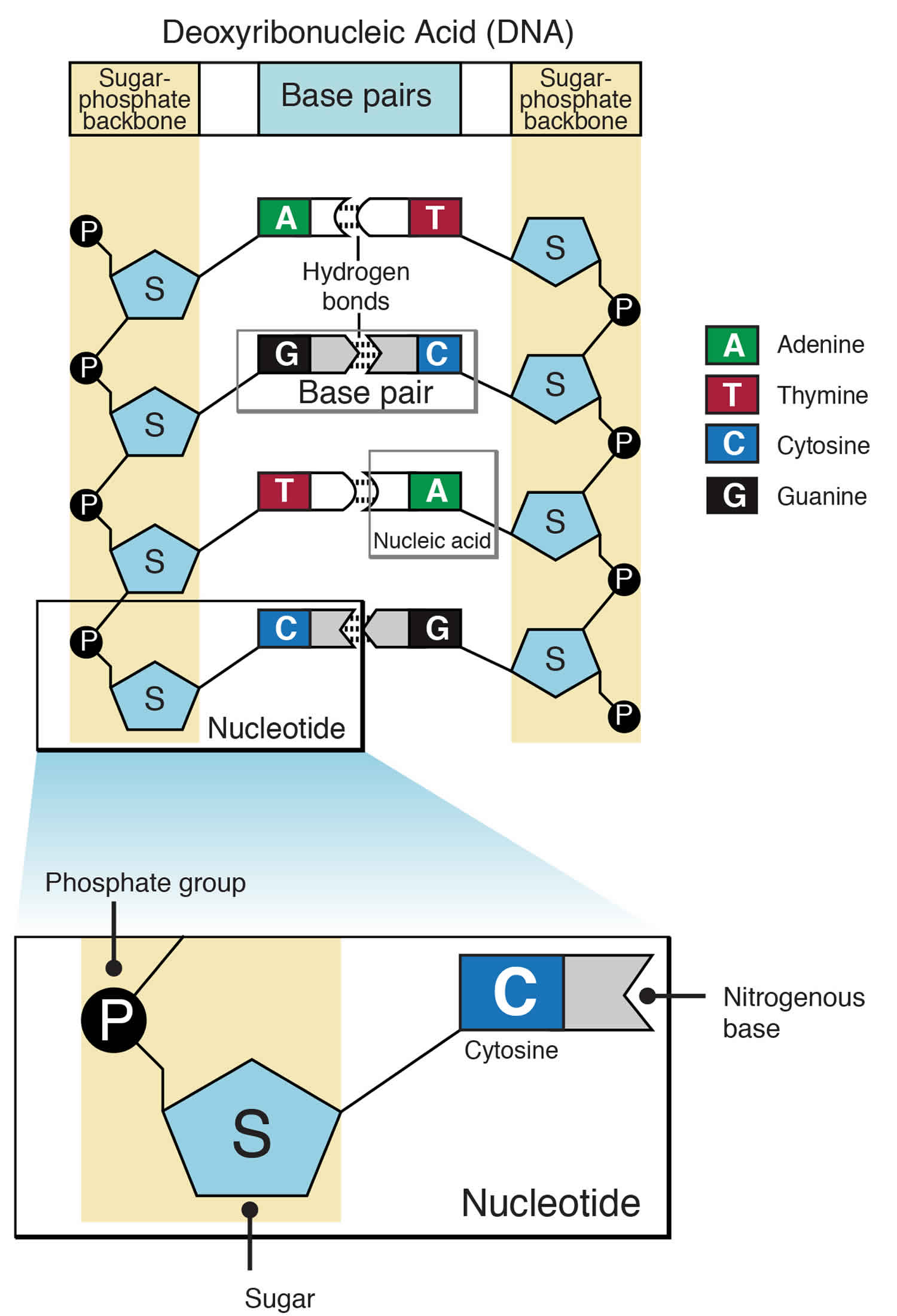
Nucleic Acids In Structure . Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Explain dna's structure and role; Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids;
from healthjade.net
Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Explain dna's structure and role; Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur.
Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
Nucleic Acids In Structure Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Explain dna's structure and role; Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing.
From www.thoughtco.com
Nucleic Acids Structure and Function Nucleic Acids In Structure Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and Nucleic Acids In Structure Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Explain dna's structure and role; Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Nucleic Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6586940 Nucleic Acids In Structure Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From www.tutorsploit.com
Nucleic Acid Types, Processes, Structure, and Differences Nucleic Acids In Structure Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Explain dna's. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From www.online-sciences.com
Molecular structure of nucleic acids Science online Nucleic Acids In Structure Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Explain dna's structure and role; Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From healthjade.net
Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types Nucleic Acids In Structure Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Explain dna's structure and role; Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Nucleic Acid Structure Nucleic Acids In Structure Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From chemistrytalk.org
Nucleic Acids ChemTalk Nucleic Acids In Structure Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From basicmedicalkey.com
Nucleic Acid Structure & Function Basicmedical Key Nucleic Acids In Structure Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Explain dna's structure and role; Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From healthjade.net
Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types Nucleic Acids In Structure Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Explain dna's structure and role; Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From www.drawittoknowit.com
Cell Biology Glossary Nucleic Acids Sugars & Bases Draw It to Know It Nucleic Acids In Structure Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From study.com
Nucleic Acid Function, Structure & Importance Lesson Nucleic Acids In Structure Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Explain dna's structure and role; Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From alevelbiology.co.uk
Nucleic Acids DNA And RNA ALevel Biology Revision Notes Nucleic Acids In Structure Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Web describe the two types of nucleic. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From sites.google.com
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal Nucleic Acids In Structure Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and Nucleic Acids In Structure Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Nucleic Acid Structure Nucleic Acids In Structure Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Explain dna's structure and role; Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From www.thoughtco.com
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers Nucleic Acids In Structure Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Elemental analysis of nucleic acids showed the presence of phosphorus, in addition to the usual c, h, n & o. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that. Describe the secondary structure of dna and. Nucleic Acids In Structure.
From open.lib.umn.edu
3.4 Nucleic Acids The Evolution and Biology of Sex Nucleic Acids In Structure Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Explain dna's structure and role; Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids contained no sulfur. Web describe nucleic acids' structure and define the two types of nucleic acids; Web describe the two types of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids In Structure.